* This product is for research use only. Not intended for use in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
| Catalog | Product Name | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|
| BT-000020 | Neuro-Transfection Reagent | Inquiry |
| BT-000021 | Neuro-2a Transfection Reagent | Inquiry |
| BT-000022 | Astrocytes Transfection Reagent | Inquiry |
Efficient delivery of genes to neurons is an important tool for studying neuronal cell biology and for developing novel therapeutic agents. Find Neuro-transfection Kits with low toxicity at BOC Sciences!
Neuron cells are nerve cells, the most basic structural and functional unit of the nervous system, divided into two parts:
The cell body consists of nucleus, cell membrane, and cytoplasm, and has the function of connecting and integrating incoming and outgoing information.
There are two types of protrusions: dendrites and axons. Dendrites are short and multi-branched, extending and protruding directly from the cell body to form dendrites. Their function is to accept the impulses from the axons of other neurons and transmit them to the cell body. The axon is long, with few branches, and is an elongated protrusion of uniform thickness. In addition to the branches of the axon, the ends of the axons form branch-like nerve endings. The endings are distributed in some tissues and organs, forming various nerve ending devices. Sensory nerve endings form various receptors; motor nerve endings are distributed in skeletal muscles to form the ultimate movement.
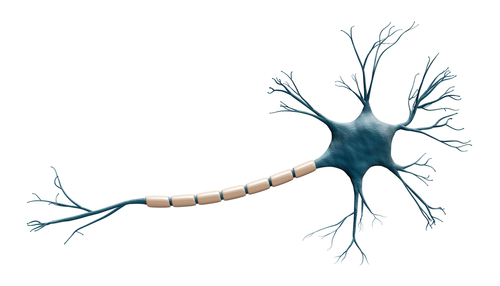 Fig. 1 Structure of Neuron cell
Fig. 1 Structure of Neuron cell
| Products | Cell Types | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Neuro-Transfection Reagent | Primary nerve cells, glial cells, and cultured nerve cell lines |
|
| Neuro-2a Transfection Reagent | Neuroblastoma cells | |
| Astrocytes Transfection Reagent | Astrocytes cells |