* This product is for research use only. Not intended for use in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
Antibody (Ab) is a spherical protein with a Y-shaped structure secreted by effector B cells and used by the body to defend itself against foreign substances such as viruses, bacteria and other antigens. It is found only in the blood and the membrane surface of B-lymphocytes in vertebrates. Any substance that can bind to an antibody is called an antigen, so in the case of anti-antibodies (antibodies that bind to antibodies), the antibody itself is also an antigenic substance.
The current common classification classifies common antibodies into five categories according to their physicochemical properties and biological functions.
IgG is a major Ig in serum, accounting for about 65-75% of total Ig. IgG is widely distributed in tissue fluid, and the distribution in intravascular and extravascular spaces is roughly equal. It is an important substance in the body's anti-infection.
IgM is the first type of Ig synthesized by the mature fetus, and it is also the earliest Ig produced after infection or immunization. Among the five types of Ig, IgM is the strongest, so its cytotoxic activity and cytolytic activity are also the strongest. The natural blood group antibody is IgM, and some autoantibodies such as antiphospholipid antibodies and RF also belong to IgM.
The content of IgA in serum and tissue fluid is relatively small. The content of serotype IgA accounts for 15-25% of the total Ig, but the content is higher in exocrine fluids such as colostrum, saliva, tears, intestinal secretions and bronchial secretions. Since IgA is mainly present in the exocrine fluid, it plays an important role in the first-line defense against infection.
IgE is a monomeric structure and is the least abundant Ig in normal human serum. The content of IgE in serum and tissue fluid is very small, and its main biological function is to bind to specific receptors on the surface of tissue mast cells and basophils. IgE cannot activate complement.
The concentration of IgD in normal human serum is very low and almost undetectable. IgD mainly exists on the surface of human B lymphocytes as a cell receptor for antigens. The content of IgD in serum is very small and the IgD bound to the membrane has different structures.
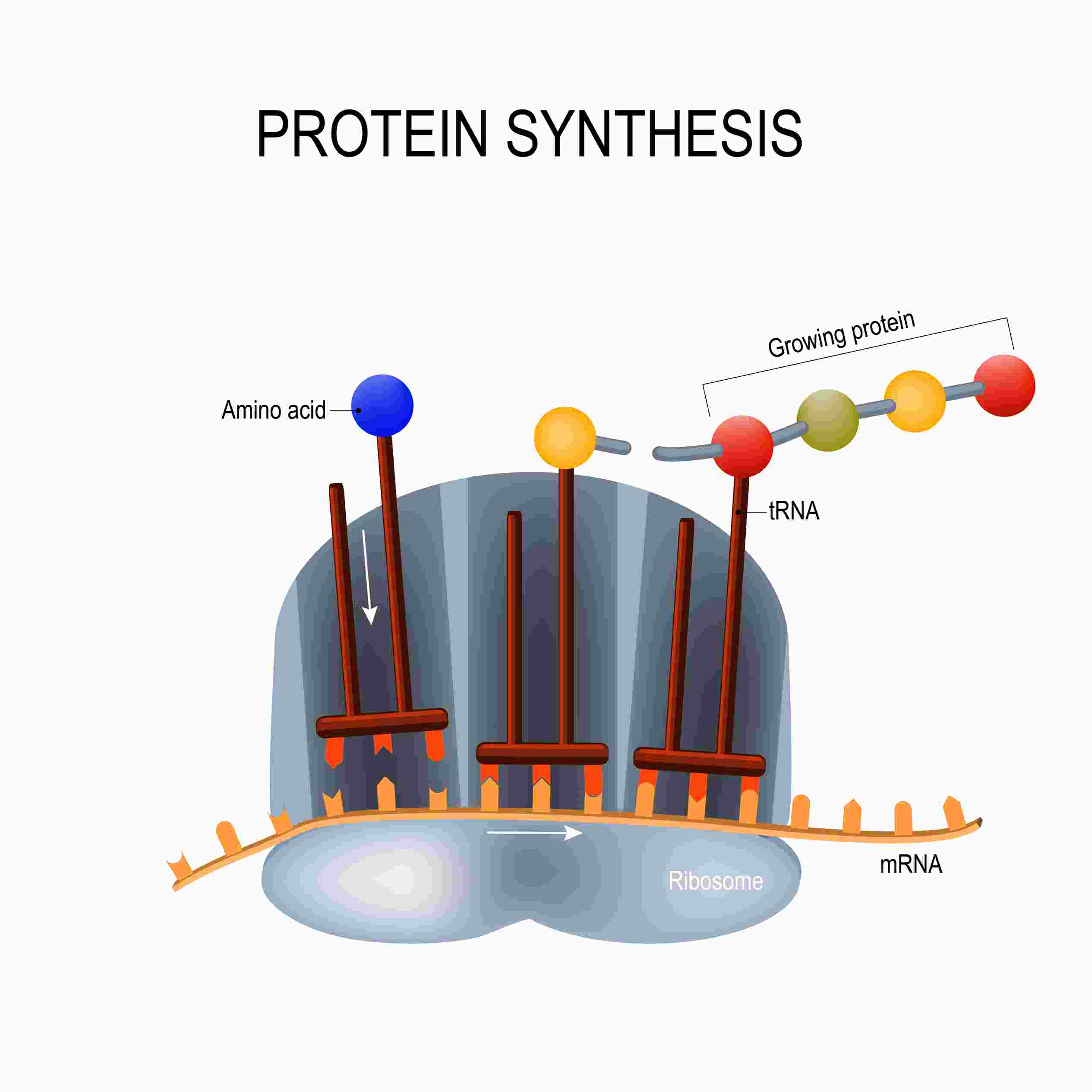
Proteins are large biological molecules, or macromolecules, that consist of one or more long chains of alpha-amino acid residues. The α-amino acid molecules are arranged linearly, with the carboxyl and amino groups of adjacent α-amino acid residues linked together by peptide bonds and finally folded to form a functional three-dimensional structure. The α-amino acid sequence of a protein is encoded by the corresponding gene.
Proteins are made up of C (carbon), H (hydrogen), O (oxygen), N (nitrogen) and generally proteins may also contain P (phosphorus), S (sulfur), Fe (iron), Zn (zinc), Cu (copper), B (boron), Mn (manganese), I (iodine), Mo (molybdenum), etc.
The antibody/protein drug industry has been growing rapidly in recent years and has taken on an extremely important role in the field of anti-tumor and autoimmune therapies. The global market for antibody/protein drugs is large and has a promising future, and is one of the highest compound growth rates in biopharmaceuticals. With further research and breakthroughs in antibody/protein drugs, the therapeutic areas will be further expanded. Transfection reagents are widely used in antibody/protein development. Based on the needs of the industry, BOC Sciences provides a variety of transfection reagents for different project needs. Biomolecules can be efficiently delivered through advanced formulations and optimized transfection methods.
| Products | Description |
|---|---|
| DNA Transfection Kits | Our products can safely and effectively deliver plasmid DNA and virus DNA into mammalian cells, so that you can get more reliable results in your studies. |
| In Vivo Transfection Reagent | High efficiency, low toxicity transfection reagent for DNA, siRNA, mRNA, and other oligonucleotides. |
| Protein Transfection Kits | Used to directly transfect the protein itself into mammalian cells, instead of transfecting DNA or mRNA encoding the protein of interest. |
| Cell Line Transfection Kits | BOC Sciences provides a variety of validated cell line transfection reagents for the field of life science research to meet the transfection requirements of different types of cell lines. |
| RNA Transfection Kits | BOC Sciences provides proven various types of RNA transfection reagents for life science research to meet different transfection requirements. |
| Electroporation Products | Electroporation, as an increasingly popular physical transfection method, uses high voltage to introduce exogenous nucleic acids into many types of cells (including bacteria and mammalian cells). |